Overview
Teaching: 10 min Exercises: 0 minQuestions
What are some widely used machine learning algorithms?
What category do they belong to?
Objectives
Gain an conceptual understanding of some example machine learning algorithms
Linear Regression
(Supervised learning, regression)
-
Yes, algorithms as simple as linear regression can also be considered as machine learning!
-
Simplest regression algorithm with numerous applications
-
A good first try for regression problems (it’s good idea to start with simple models to understand the data better before building complicated ones!)
-
Multivariate linear regression: linear regression with multiple input variables

Figure: Illustration of linear regression (image source: https://machinelearning-blog.com/2018/01/24/linear-regression).

Figure: Multivariate linear regression (image source: StackExchange).
Kernel Smoother
(Supervised learning, regression)
-
Instead of fitting global data, kernel smoothers only use those input data points close to the new data point x0 and fit a simple model on these “local” input data points. Weights can be assigned to these local data points.
-
Requires little or no training; just need to wait for the target data point x0, fit a local model and predict on x0.

(image source: Hastie et al. (2016): The Elements of Statistical Learning, Second Edition, Chapter 6.
Logistic Regression
(Supervised learning, classification)
-
Don’t be fooled by its name - logistic regression is the most popular classification algorithm!
-
In a binary-outcome case, logistic regression predicts the probability of the outcome being 1 versus 0.
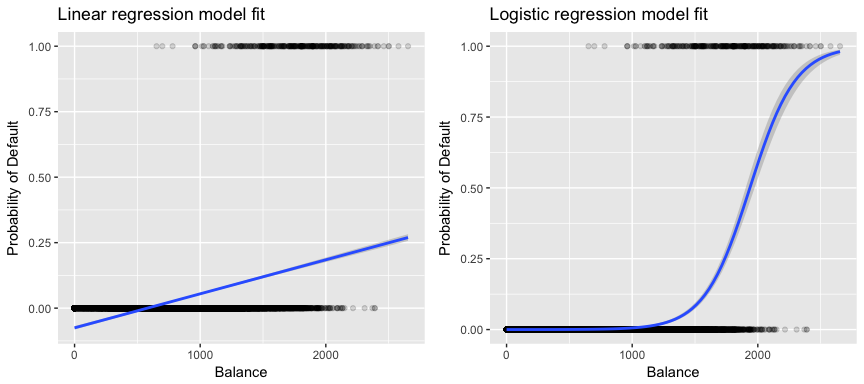
Comparison of linear regression fit and logistic regression fit for a binary outcome data set. In this example, the x-axis is the input variable, credit card balance, and the y-axis is whether or not defaulting happened (image source: http://uc-r.github.io/logistic_regression).
Decision Tree and Random Forest
(Supervised learning, classification or regression)
-
A decision tree is similar as a decision making flowchart
-
A decision tree can be learned from data by greedily choosing the input variable and finding the spliting point that best classifies the training data, repeating this process for each branch.
-
The result of a learned decision tree is intuitive to interpret.
-
A random forest is a large collective of trees.
-
It aggregates a large number of decision trees trained on a random subset of input data.
-
Can potentially result in better performance.
-
Figure: Illustration of a decision flowchart (image source: https://imgs.xkcd.com/comics/solar_panels.png).
K-Means Clustering
(Unsupervised learning)
-
Clustering methods cluster a dataset into multiple groups.
-
K-Means is one of the most commonly used clustering algorithm that iteratively updates the cluster centroids and cluster assignment for each data point. The number of clusters needs to be specified.

Illustration of clustering (image source: https://mubaris.com/posts/kmeans-clustering).
Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
(Unsupervised learning)
-
PCA is a statistical procedure that transforms a set of input data of possibly correlated variables into a set of new variables that are linearly uncorrelated (the transformed variables are called principal components). After the transformation, the first principle component accounts for as much of the variability in the data as possible, and the second principle component accounts for the largest variability in the remaining dimensions of the data that are orthogonal to (i.e., have no linear correlation with) the first principle component, and so on so forth (source: Wikipedia).
-
PCA can be used for dimention reduction (e.g., image compression)
-
PCA is widely used in atmospheric sciences, often referred to as Empirical Orthogonal Function (EOF) analysis in the field. For example, EOF can be applied on a temporal-spatial climate dataset to find the most dominant spatial and its associated temporal variation.

Figure: For a input dataset with two variables, the PCA algorithm finds the first principal component that accounts for the largest data variability (the longer vector in the figure) and the second principal component that is orthogonal to the first one (the shorter vector in the figure) (image source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Principal_component_analysis).

Figure: Example PCA application in atmospheric sciences. Here “residual SST field” is sea surface temperature from which the variability associated with the ENSO cycle has been removed (image source: Zhang et al. (2017): ENSO-like Interdecadal Variability: 1900–93, Journal of Climage).
Neural Network and Deep Learning
(Supervised or unsupervised learning, classification or regression)
-
Neural network is framework for many algorithms, vaguely inspired by the structure of animal brains.
-
A typical neural network has an input layer, one or multiple hidden layers, and an output layer. Each layer consists of a collection of units or nodes (called neuron) that are connected with those neurons in the adjacent layers via transformations (called activation functions with parameters).
-
A hidden layer can “learn” a set of new variables from the previous layer, which would be a better set of input variables for the next layer.
-
Machine learning using neural networks with many hidden layers are sometimes called deep learning.
-
There exist a large number of various constructions of neural networks, suitable for different applications.
-
A good review of neural network/deep learning applications in water resources research: Shen (2018): A transdisciplinary review of deep learning research and its relevance for water resources scientists, Water Resources Researh.

Figure: Illustration of a neural network with two hidden layers (image source: https://www.digitaltrends.com/cool-tech/what-is-an-artificial-neural-network).
Key Points
Machine learning algorithms